InstructGPT — The Complete Guide:
InstructGPT transformed instruction-following in large language models by reframing the problem as preference alignment rather than raw scale-only performance. Instead of relying solely on larger parameter counts or complicated prompt engineering, InstructGPT uses human demonstrations and comparative judgments to shape model behavior so outputs align with what people find useful, safe, and context-appropriate. In natural language processing (NLP) terms, this is an alignment-by-supervision strategy, where supervised fine-tuning provides a conditional distribution baseline and a learned reward model supplies a scalarized human preference function. Reinforcement learning (commonly PPO) then moves the policy toward regions of higher expected human reward under a divergence constraint.
For practitioners and product engineers, InstructGPT is a reproducible pipeline: collect structured demonstration pairs, build a reward predictor from pairwise rankings, and apply policy optimization with regularization. The result is a model that better maps instruction tokens to desired output distributions, improves user experience for instruction-driven features (summaries, rewrites, constrained outputs), and reduces certain unsafe behaviors—though it does not solve all failure modes. This guide frames the entire pipeline in NLP terminology, gives practical recipes for prompting and integration, and reviews limits, evaluation metrics, and implementation checklists you can use to build production-grade instruction-tuned systems.
What is InstructGPT?
InstructGPT refers to a family of transformer-based language models that have undergone instruction tuning—the process of adapting a pretrained next-token model to follow natural-language directions better. In formal notation:
InstructGPT is not a single checkpoint name but a reason for the general SFT→RM→RL pipeline. Its goal is to approximate the conditional distribution π∗(y∣x)\pi^*(y \mid x)π∗(y∣x) implicit in human knowledge, making the model produce high-quality, context-appropriate responses to explicit law.
Key conceptual pillars, InstructGPT
- Lesson-focused: Align the model to map natural instructions to desired responses.
- personal-in-the-loop: Use human-written test and pairwise rankings as supervisory signals.
- Adjustment-oriented: Optimize for human preference and reduce unhelpful or harmful outputs while retaining the generation.
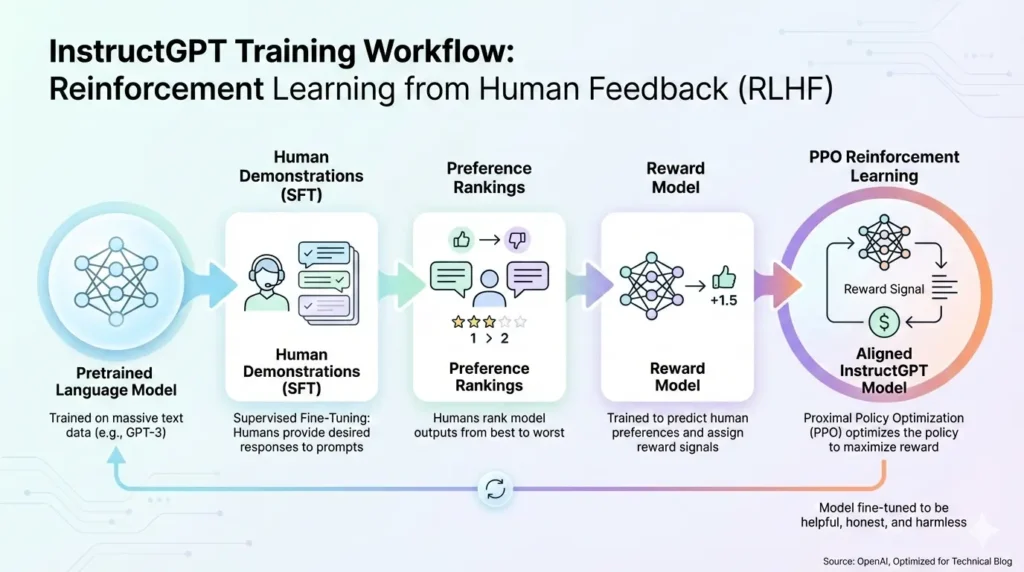
The RLHF Training Pipeline
Below is the practical pipeline most teams use to produce InstructGPT-style models, expressed with NLP formalisms and practical notes.
Collect Demonstration Data InstructGPT
What you collect.
A dataset of pairs (xi,yidemo)(x_i, y_i^\text{demo})(xi,yidemo) where each xix_ixi is an instruction/context and yidemoy_i^\text{demo}yidemo is a high-quality human response. Demonstrations encode not only content but tone, length, formatting, and preferred error modes (what to leave out).
Why it Matters.
The demonstrations define the supervised conditional distribution used to initialize the tuned policy. Diversity across prompts and demographics reduces overfitting to narrow styles.
Practical Tips.
- Ensure labeler guidelines are explicit: Desired tone, factuality threshold, citation behavior, and PII handling.
- Use multiple labelers and consensus processes for high-impact categories (medical, legal).
- Format canonical responses for structured outputs (JSON, bullet lists) to improve downstream extraction.
Supervised Fine-Tuning
Fine-tune a pretrained autoregressive language model on the (x,ydemo)(x, y^\text{demo})(x,ydemo) pairs, typically using teacher-forcing and cross-entropy loss:
What Happens.
LSFT(θ)=−∑tlogpθ(ytdemo∣y<tdemo,x)\mathcal{L}_\text{SFT}(\theta) = -\sum_{t} \log p_\theta(y_t^\text{demo} \mid y_{<t}^{\text{demo}}, x)LSFT(θ)=−t∑logpθ(ytdemo∣y<tdemo,x)
NLP Framing.
SFT biases the model toward the human conditional distribution pSFT(y∣x)p_\text{SFT}(y \mid x)pSFT(y∣x), improving instruction compliance but not necessarily optimizing for human preference ranking beyond the demonstration style.
Notes.
- Use data augmentation sparingly (paraphrases of instructions help generalization).
- Monitor token-level loss and generation quality metrics.
Reinforcement Learning (PPO) to optimize policy
Setup.
Treat the SFT model as an initial policy πθ(y∣x)\pi_\theta(y \mid x)πθ(y∣x). Use the learned reward rϕ(x,y)r_\phi(x,y)rϕ(x,y) as the scalar RL reward, and perform policy optimization to increase expected reward.
Why PPO?
PPO (carePolicy Optimization) is widely used because it provides fast policy updates with clipping pressure. Crucially, teams include a KL-penalty or constraint to avoid the policy drifting too far from the pretrained mean distribution ppre(y∣x)p_\text{pre}(y \mid x)ppre(y∣x):
Practical Recipe.
- Use distributed rollouts to sample responses, compute rewards via the RM, and update policy via PPO’s clipped surrogate objective.
- Monitor KL divergence during training; target a small, stable divergence to preserve base capabilities.
- Include entropy bonuses to retain diversity if needed.
Evaluation & iteration InstructGPT
Human evals and metrics.
- Human preference win-rate (fraction of comparisons where the RLHF model is preferred over the baseline).
- Safety incident rate (toxic outputs per 1k prompts).
- Hallucination frequency (measured on a benchmark of verifiable prompts).
- Downstream task success (task-specific metrics like extractive QA F1).
Iterate. For failure modes, collect new demonstrations/rankings focused on those cases, retrain RM, and continue.
Short summary in pipeline form.
SFT → RM → PPO (with KL) — the canonical ordering that yields instruction-aligned policies.
Why InstructGPT Matters
Better instruction-following
Instruction-tuned models map instruction tokens to desired conditional distributions more reliably; empirically, they require fewer prompt-engineering hacks (chain-of-thought prompts, manual constraints) to perform fixed-format tasks.
Cost-Efficiency
In many human-evaluation metrics, smaller instruction-tuned models can match or exceed larger baseline models due to targeted alignment—i.e., the model’s useful behavior is improved without scaling parameter count proportionally.
Safer outputs InstructGPT
RLHF tends to reduce some categories of unsafe outputs (obvious toxic language, incitement) when the RM is trained with safety-focused comparisons. However, this is a relative reduction, not elimination.
Product UX improvements InstructGPT
Because instruction-tuned models accept direct commands (“Summarize”, “Rewrite as bullets”, “Translate to X”), they enable simpler UI building blocks (buttons, short prompts) and more predictable text transformations.
Limitations, failure modes, and ethical concerns
Bias and cultural assumptions
Human labelers’ backgrounds shape what the RM treats as “preferred.” If labeler demographics are narrow, the RM will encode cultural priors that skew outputs—e.g., tone preferences, idioms, or controversial content moderation decisions.
Mitigations.
- Use demographically diverse labeler pools.
- Include bias-detection tests and counterfactual data augmentation.
Reward misspecification and over-optimization
A reward model is an imperfect proxy for reality. Optimizing policy to maximize an imperfect reward can produce degenerate behavior (exploiting artifacts, producing outputs that “look good” to the RM but are wrong or manipulative).
Technical caution.
This is a form of specification gaming; include adversarial evaluation and human-in-the-loop checks on high-reward edge cases.
Hallucinations Remain InstructGPT
Instruction tuning reduces but does not eliminate hallucination. A high-reward but factually wrong answer can still be favored if RM preferences emphasize fluency or confidence over verifiable correctness.
Mitigation:
Use retrieval augmentation, grounding to knowledge sources, or entailment-based verification before releasing high-stakes content.
Transparency and audit gaps
Public papers often omit detailed labeler guidelines, exact datasets, or RM hyperparameters, complicating third-party audits and reproducibility.
Recommendation: Publish model cards, labeler instructions, and evaluation datasets when possible.
Data & privacy Risks
If demonstration or ranking datasets include private or copyrighted information, models can memorize and regurgitate it. Use PII redaction and differential privacy techniques where appropriate.
Long-Tail behavior and Robustness
Instruction tuning improves median-case behavior but may not cover rare, adversarial, or domain-specific instructions. Test on real prompt distributions and perform stress testing.
Few-Shot for Rare Tasks
Provide 1–3 concise examples for unusual or domain-specific tasks. Usually, instruction tuning reduces the need for few-shot demonstrations; use them when the task is highly atypical.
Tips: Always specify tone, format, and length; validate outputs for fact-critical tasks.
InstructGPT vs GPT-3 vs ChatGPT
- GPT-3 (base): Objective: Next-token likelihood. Strength: broad generation. Weakness: needs prompt engineering to fulfill structured instructions.
- InstructGPT: Objective: Aligned to human preferences via RLHF. Strength: structured, instruction-focused outputs. Weakness: Relies on RM quality; not conversationally stateful.
- ChatGPT: Objective: Instruction alignment + conversational context handling + further safety tuning and moderation layers. Strength: chat UX, multi-turn coherence. Weakness: heavier safety layers may reduce certain creative outputs.
Takeaway: Use instruction-tuned models for deterministic instruction-driven functions (summaries, rewrites). Use conversational models for chat interfaces requiring persistent context and multi-turn grounding.
Evaluation and metrics you should track
- Human preference win rate: How often humans prefer the tuned model over the baseline.
- Safety incident rate: Count of harmful or policy-violating outputs per 1,000 prompts.
- Hallucination frequency: Rate of factually incorrect claims on a verifiable benchmark.
- Latency & cost per request: Engineering-level SLOs and budget projections.
- User comfort task success: Product metrics (completion rates, retention) on real users.
Note: Personal evaluations are the gold standard; automated proxies are useful but must be validated against human reasoning.
Pros & cons InstructGPT
Pros
- Improved instruction following and predictable behavior.
- Better safety on many axes when combined with filters.
- Cost-effective: Smaller tuned models can deliver aligned performance.
Cons
- Hallucinations persist.
- Labeler bias can be encoded.
- Requires human labeling infrastructure (time + cost).
- Opaque training details can hinder external audits.
FAQs InstructGPT
A: Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback. It uses human preference signals to train a reward model and then optimizes the language model to maximize that reward.
A: No. “InstructGPT” refers to models produced by instruction-tuning methods (SFT→RM→PPO). OpenAI released papers and APIs that use this method, and other teams implement similar pipelines.
A: No. It reduces some unsafe or irrelevant behavior but does not eliminate hallucinations. Use verification steps and post-filters for critical tasks.
A: Commonly, PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization) is used, with a KL penalty to the pretrained policy to avoid drift.
A: You can start small, but reward modeling and human ranking quality are crucial. The more diverse and high-quality the human feedback, the better the reward model will generalize.
A: RLHF helps make models more aligned, but safety depends on labeler instructions, dataset quality, post-filters, and human review workflows.
Conclusion InstructGPT
InstructGPT shows how instruction tuning with RLHF makes language models more useful, predictable, and aligned with human intent. By linking supervised fine-tuning, reward modeling, and PPO, it enables clear instruction-following without heavy construction. Although challenges like hallucinations and bias stop, careful evaluation, guardrails, and human oversight make InstructGPT-style models a practical and effective base for modern products.

