GPT-3 The Definitive Guide
GPT-3 is an autoregressive large language model introduced by OpenAI that demonstrated how model scale and transformer architectures enable powerful in-context learning for many natural language tasks. With roughly 175 billion parameters and trained to minimize next-token prediction loss on large web-scale corpora, GPT-3 serves as a flexible limited language generator: the conditional distribution of extension. In fact, it shifted weight from supervised duty-specific training toward a few-shot and zero-shot reward system via engineering, permissive summarization, classification, structured extraction, code generation, and more, without bank updates. however using GPT-3 in production requires kind sampling mechanics, tokenization, and context windows, hallucination danger, bias amplification, and cost-per-token tradeoffs. This guide defines GPT-3 in terms of architecture, objectives, annals, attention, gives production-ready API patterns and recipes, fair opinion and monitoring strategies, and adds an operational checklist for safe distribution, cost control, and reproducible channel.
What is GPT-3?
GPT-3 seates for Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3. In terms, it is a large-scale, scholar-only Transformer trained with a creative language modeling objective: maximize the likelihood of the next token given previous tokens. The model learns a defined conditional chance distribution Pθ(xt∣x1..t−1)P_\theta(x_t \mid x_{1..t-1})Pθ(xt∣x1..t−1) across a big vocabulary of byte-pair encoded tokens. as it is trained on grand unlabeled text and scaled to hundreds of billions of domain, GPT-3 demonstrates budding capabilities: they can perform tasks by conditioning on part and instructions presented in the input string, without parameter updates for task removel.
- Building: Decoder-only tool with multi-head self-attention and feed-forward layers.
- cool: Unusual language modeling.
- Transfer mechanism: In-context learning (few-shot), not classic fine-tuning.
- Tokenization: Subword (BPE/tokenizer) producing tokenized sequences that determine context window usage.
Why GPT-3 Mattered
- Scale unlocks generalization: Scaling parameter count and training data demonstrated improved zero-/few-shot performance on many NLP tasks, suggesting model capacity partly substitutes for task-specific supervision.
- Prompt-first paradigm: Task specification moved from changing model weights to engineering input prompts that elicit desired behaviors. Practitioners can now shape model outputs at inference time.
- API-driven adoption: Making the model available via API enabled rapid integration into products and research without expensive infrastructure.
- Shift in evaluation: Benchmarking began to emphasize few-shot performance, robustness across prompts, and downstream practical utility rather than single-task fine-tuned state-of-the-art metrics only.
How GPT-3 works
The Short, Technical Special Explanation
- Transformer building piece: Multi-prime attention, positional encodings, layer norms, and enduring connections. The mind computes context-dependent contextualized representations; feed-forward layers apply a non-linear shift.
- Therapy: killed on massive unlabeled corpora to minimize cross-entropy loss for next-token guess. This produces strong lexical, syntactic, and some semantic knowledge.
- Inference: provide a prompt; decode tokens autoregressively using sampling (temperature, top-k/top-p) or greedy/deterministic decoding. Outputs are sampled from the learned conditional distribution.
Key Technical Behaviors
- Autoregression: Token-by-token generation conditioned on prior tokens.
- In-context learning: The model implicitly learns from examples provided in its context without gradient updates.
- Finite context window: The model can meaningfully use only the last NNN tokens (context length); tokens older than that are truncated.
- Sampling & determinism: Temperature and nucleus/top-p sampling modulate output entropy; temperature near 0 reduces randomness.
Pricing, Cost Control & Deployment Tradeoffs
APIs bill per token; both input and output tokens count. Larger, more capable models cost more per token. Consider the following strategies:
Cost Control Strategies
- Cache repeated queries: Reuse outputs for identical prompts.
- Truncate history: keep only salient dialogue context in conversational systems.
- Use smaller models for simple tasks: reserve large models for tasks with high complexity or where quality gains matter.
- Batch tasks: Ask the model to process multiple items in one call (e.g., 50 short summaries in a single prompt).
- Set sensible max_tokens: Constrain maximum output length and use stop sequences.
Pricing Example
Pricing changes; always consult provider docs for up-to-date rates. Build calculators that estimate expected monthly tokens from per-user interactions to forecast cost.
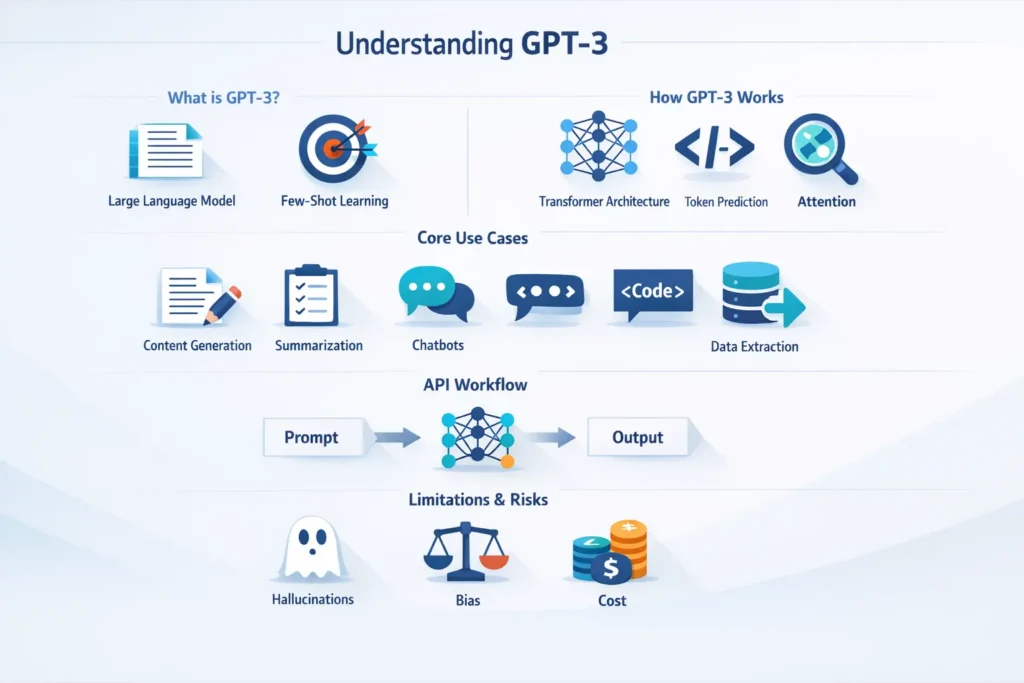
Limitations & Risks
GPT-3 is powerful but not infallible. In production systems, guardrails are necessary.
Hallucinations
The model can generate fluent but incorrect or fabricated statements. Mitigations:
- Use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG): supply verified context as part of the prompt.
- Post-verify model facts against authoritative sources.
- Use conservative decoding and ask the model to cite sources (but citations are not guaranteed to be correct).
Bias & Fairness
Models learned statistical patterns from web corpora, so outputs can reflect social biases. Mitigations:
- Audit model outputs for biased patterns across demographics.
- Use filters, post-processing, and human review on sensitive outputs.
Privacy & input care
Avert sending sensitive special data to third-party APIs unless you have contractual assurances and understand data retention policies. As ruled data, consider on-premise or private model distribution.
Reproducibility & Determinism
Random sampling introduces variability for reproducible outputs. Set the temperature to 0 and use deterministic decoding where possible.
Intellectual Property & Provenance
The training data composition is opaque; be cautious about outputs that could reproduce copyrighted text. For legal-sensitive tasks, add provenance & human review.
Evaluation & Metrics
Evaluate LLMs both automatically and with human raters.
Automatic Metrics
- Perplexity: Measures how well the model predicts held-out text (lower is better). Useful during training comparisons.
- BLEU / ROUGE / METEOR: For some generation tasks (translation, summarization) — limited for capturing semantic quality in open-ended generation.
- Exact match / F1: For structured extraction tasks.
Human Evaluation
- Fluency, adequacy, factuality, helpfulness, safety. Use task-specific annotation guidelines and multiple annotators.
- A/B testing: Measure end-user metrics (task completion rates, retention, time saved).
Operational Monitoring
- Latency & error rates.
- Hallucination frequency: Spot-check outputs for factuality.
- Bias & toxic content rate: Track and measure over time.
- Cost per successful outcome: Combine cost metrics with business KPIs.
When to Use GPT-3 vs Newer Models
GPT-3 remains useful for prototypes and various generation tasks, but newer model families (e.g., GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and brood) are all over:
- Better instruction following
- Improved factuality and reasoning
- Larger context windows
- Multimodal capabilities (in some variants)
Decision Rule of Thumb:
- If the duty requires advanced thinking, long-context RAG, or higher factual reliability, check next-generation models.
- For rapid prototyping and low-budget use, GPT-3 variants may suffice.
Comparison Table: GPT-3 vs Next-Generation Models
| Model | Year (Initial) | Typical Strengths | Typical Limitations |
| GPT-3 | 2020 | Strong general text gen; few-shot learning | Hallucinations; smaller context; older instruction-following |
| GPT-3.5 | 2022 | Better instruction following; improved chat handling | Still probabilistic; cost is higher than tiny models |
| GPT-4 / later | 2023+ | Improved reasoning, multimodal options, and larger context windows | More expensive; evaluate per task |
Note: model names, capabilities, and pricing change rapidly — always consult official docs.
Deployment Checklist
Before shipping an LLM-powered feature:
- Define intent & risk profile — is this prototype or high-stakes production?
- Choose model & cost baseline — estimate token usage and expected monthly calls.
- Build prompt templates — store canonical prompt formats and test edge cases.
- Implement safety filters — profanity, PII masking, hate-speech classifiers.
- Human-in-the-loop — route high-risk outputs to human reviewers.
- Monitoring & metrics — latency, hallucination rate, cost per transaction.
- Fallback & escalation — scripted responses and backoff strategies.
- Iterate & retrain — collect failure cases and refine prompts or fine-tune specialized models.
Pros & Cons
Pros
- Rapid prototyping via prompts.
- Large ecosystem and API access.
- Versatile across many text tasks.
Cons
- Hallucinations can cause factual errors.
- Cost can be high at scale.
- Privacy and compliance concerns for sensitive data.
Real-World Checklist for Production Safety
- PII removal: Srub or anonymize personal data before sending to external APIs where possible.
- Rate limits: Implement per-user rate limiting and token budgets.
- Audit logs: Log prompts and outputs for debugging and compliance (mask sensitive fields in logs).
- Human review: Route high-impact domain outputs (medical, legal) to specialists.
- User disclaimers: Mark AI-generated content and provide correction flows.
FAQs
A: GPT-3 is a large autoregressive transformer model from OpenAI (released 2020). It showed strong few-shot learning and wide text generation ability.
A: Use OpenAI’s API: send prompts, pick a model, set parameters (temperature, max_tokens), parse the returned text, and validate outputs. Use caching and smaller models to save cost.
A: Yes — for many prototypes and generation tasks, it remains useful. But newer models may offer better accuracy and cost tradeoffs; always compare current models.
A: Use retrieval-augmented generation (supply verified documents), lower temperature, ask for structured output (JSON), add human review, and validate outputs automatically.
Final notes
- Start small: pilot one critical flow, measure cost and error rates.
- Add human review where a wrong output is costly.
- Use the prompt patterns above to improve outputs quickly.
- Keep monitoring for new model releases — occasionally, a newer model will be more accurate or cost-effective for your workload.

