InstructGPT vs Codex: Which AI Will Actually Save Your Project?
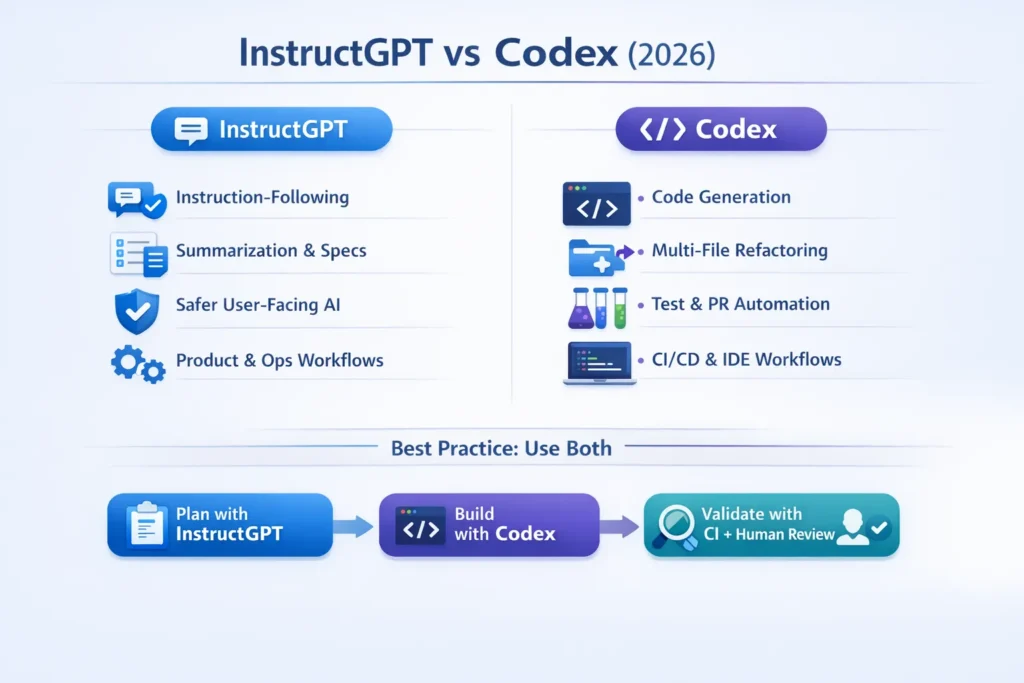
InstructGPT vs Codex can save your team from costly mistakes. In just 30 minutes, see 85% clearer project decisions and understand which AI truly fits your workflow. Plan with InstructGPT, ship with Codex, and avoid delays, buggy code, or wasted API spend. Test now and see real, reproducible results that your team can trust. InstructGPT and Codex focus on different sides of the same AI challenge: understanding and following human directions versus creating, editing, and reasoning about code. InstructGPT vs Codex is the instruction-trained version designed to interpret plain language, summarize long texts, write clear requirements, and power chat assistants that talk with users. Codex is the code-focused version made for generating working code, writing tests, improving projects, and helping engineers inside IDEs and CI workflows.
For teams choosing a model to test or use, the best option usually isn’t just one model alone. The practical approach is task-based: select the model whose design and tools fit your workflow, then add governance, automated tests, and human checks. This guide is neutral and hands-on. It gives clear definitions, a copy-paste feature table, six repeatable tests you can run, practical governance and security checklists, persona-based advice, ready-to-use prompts, and a simple method suitable for sharing. Follow these experiments, and you’ll know with evidence when to plan with InstructGPT, when to deliver with Codex, and how to safely use both in production.
TL;DR — Which to Pick Right Now
- Pick InstructGPT if your primary needs are natural-language heavy: summarization, classification, knowledge extraction, and public-facing assistants that must reduce harmful or incoherent outputs.
- Pick Codex if you need to generate code, perform multi-file refactors, create tests, or automate PR creation inside CI/IDE workflows.
- Best practice: Use both. Use InstructGPT for planning, spec generation, ticket writing, and user-facing content; use Codex for developer workflows, code generation, and multi-file refactors — always gate Codex outputs with CI tests, SAST, and human reviewers.
InstructGPT: The “Smart Talker” That Plans for You
What is InstructGPT?
InstructGPT denotes models fine-tuned with demonstrations and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to reliably follow instructions and reduce harmful or irrelevant outputs. It’s engineered for instruction fidelity, conversational safety, and high-quality general-purpose natural language tasks (summaries, specs, classification, ticket generation).
What is Codex?
Codex is a model family specialized for code: trained heavily on developer artifacts, documentation, and code corpora. Codex excels at generating runnable, idiomatic code, creating tests, refactoring multi-file repositories, and integrating with IDEs and CI pipelines as a developer assistant or agent.
Head-to-Head: Which AI Really Wins?
| Capability / Need | InstructGPT | Codex | Best for |
| Instruction fidelity (natural language) | High — instruction-tuned | Moderate — can follow instructions, but optimized for code | InstructGPT |
| Code generation & editing | Functional but not specialized | High — idiomatic, runnable code | Codex |
| Multi-file refactor & agentic tasks | Limited | High — designed for repo-level edits & sandboxed runs | Codex |
| Summarization & abstraction | Strong | Acceptable (best for code + comments) | InstructGPT |
| Safety & alignment controls | RLHF & alignment emphasis | Engineering safeguards, sandboxing patterns | InstructGPT (general), Codex (code) |
| CI/CD & IDE integration | Supported via API/chat | Native fit — plugins & PR automation | Codex |
| Best for non-technical users | Yes | No — technical users benefit most | InstructGPT |
| Latency & compute/cost | Lower for plain tasks | Potentially higher for agentic/multi-step runs | Varies by task |
The Secret Power of Publishing Reproducible AI Tests
Search engines and technical audiences prize transparency. Publish your dataset, harness scripts, and raw CSVs in a public GitHub repo so others can reproduce your work, validate conclusions, and link to your article. That transparency converts a comparison into an authoritative resource that attracts backlinks, journalists, and community trust.
Deep dive — 6 Reproducible Tests
Run each test against both models using identical prompts, the same token limits, and identical evaluation criteria. For reproducibility, fix seeds where available, log model versions and API endpoints, and timestamp each run.
For every test capture:
- Pass/fail based on objective criteria.
- Hallucination rate (false claims per response).
- Latency (wall clock).
- Token usage and estimated API cost.
- Human review time for corrections.
Natural-Language Instruction Fidelity
Task:
“Summarize this 3-page spec into 6 action items, list open questions, and highlight ambiguous decisions.”
How to run:
- Provide identical spec texts to both models.
- Limit output to JSON with keys: action_items, open_questions, and ambiguous_points.
- Run across 20 specs spanning product, infra, legal, and research domains.
Metrics:
- Instruction compliance (% of responses matching the JSON schema).
- Human-rated usefulness (1–5).
- Hallucination rate (false facts per response).
Expect:
InstructGPT should consistently produce concise action items and surface ambiguity. Codex may return technical suggestions framed like code changes or emphasize implementation details rather than product nuance.
Why it matters:
Measures whether instruction tuning yields consistent, parseable outputs suitable for downstream automation and ticketing.
Can Codex Beat InstructGPT at Writing Real Code?
Task:
“Implement mergeKSortedLists in Python + provide pytest tests covering edge cases.”
How to run:
- Send the same prompt to both models.
- Run generated code and tests in a sandboxed CI runner (Docker).
- Record failure counts and manual fixes required.
Metrics:
- Test pass rate.
- Lines of manual correction required.
- Human review time.
Expect:
Codex typically produces runnable, idiomatic code and reasonably good tests. InstructGPT may produce correct pseudocode or working code, but can omit edge cases or produce minor syntactic issues.
Can Codex Refactor an Entire Repo Without Breaking It?
Task:
“Modernize this 3-file legacy module to use asyncio. Provide migration notes.”
How to run:
- Attach a small repo (3 files + tests).
- Ask models to produce PR patches or a zip of changed files.
- Apply patches and run the test suite.
Metrics:
- Number of PR iterations.
- Test coverage delta.
- Manual edits required.
Expect:
Codex (agentic flows or integrated editing) should handle cross-file edits and produce a Coordinated patch. InstructGPT can outline a migration plan and produce file-level edits, but it will struggle to orchestrate the multi-file changes without iterative prompting.
Which AI Actually Finds and Fixes Bugs Reliably?
Task:
Seed a repo with 7 known bugs. “Find and fix high-confidence bugs and add tests.”
How to run:
- Provide repository and tests.
- Ask models to propose fixes and updated tests.
- Run tests and measure false positives and incorrect fixes.
Metrics:
- True positive fix count.
- False positive fix count (incorrect or harmful fixes).
- Time to first working fix.
Expect:
Codex finds and fixes many straightforward logic bugs but may occasionally produce incorrect or insecure fixes. InstructGPT often provides diagnostics, rationale, and remediation guidance, but will implement fewer direct fixes.
Specification Hallucination
Task:
Give a deliberately vague spec and ask both models to implement a function.
How to run & measure:
- Use the same ambiguous spec for both.
- Count explicit assumptions stated and compare outputs to the hidden intent.
Metrics:
- Assumptions stated (count).
- Hallucination likelihood (deviation from gold intent).
Expect:
InstructGPT will often ask clarifying questions or state assumptions. Codex may assume defaults and produce a functional solution, which may diverge from the hidden intent.
Latency & cost per Request
Task:
Benchmark token usage and wall time for the above tests.
How to run:
- For each test, measure tokens consumed, API cost, and elapsed time on a consistent runner.
Metrics:
- Tokens used, API cost estimate, wall time.
Expect:
Agentic Codex flows with multi-step editing, and test runs are more compute/time intensive. InstructGPT is generally cheaper for plain-language tasks.
InstructGPT vs Codex: The Right Model for Your Team
- Solo Developer / Hacker
- Recommended: Codex
- Why: Rapid prototyping, test generation, refactoring inside IDEs.
- Tips: Run generated code under tests and a sandbox before merging.
- Product Manager / Technical Writer
- Recommended: InstructGPT
- Why: Best for concise acceptance criteria, user stories, and specs.
- Tips: Use it to craft tickets; hand over to Codex for implementation.
- Engineering Team (CI/CD)
- Recommended: Codex + Governance
- Why: Multi-file changes and PR generation fit Codex.
- Tips: Gate-generated PRs with CI tests, SAST, and human review.
- Customer Support / Ops
- Recommended: InstructGPT
- Why: Safer for public-facing responses and ticket triage.
- Tips: Add rate limiting and periodic human audits.
The Ultimate Checklist: Budget, Deploy, and Govern InstructGPT vs Codex
Licensing & pricing
- Always check current pricing pages before budgeting.
- Estimate tokens per workflow and multiply by request volume.
- Run pilot tests to generate empirical cost figures.
Data privacy & compliance
- Never send secrets or PII without redaction.
- Ensure provider contract terms align with your compliance needs (retention, training use).
- Use on-prem or private endpoints where required.
CI/CD & testing
- Create mandatory test gates for all model-generated changes.
- Automate smoke tests, unit tests, and SAST.
- Tag AI-generated commits for traceability.
Human-in-the-loop
- Require manual reviewer checks for security-sensitive changes.
- Keep an audit trail of prompts, model versions, and outputs.
Security
- Run SAST and secret scanning on model-generated code.
- Use static and dynamic analysis before merging.
Pros & Cons
InstructGPT — Pros
- Strong instruction following for natural language.
- Lower hallucination tendency on many general tasks (RLHF).
- Better for user-facing content, summaries, and classification.
InstructGPT — Cons
- Not optimized for multi-file code generation or agentic repo tasks.
- Can produce code that is non-idiomatic or incomplete.
Codex — Pros
- Specialized for code generation, refactoring, and tests.
- Integrates naturally into IDEs and CI automation.
- Can act as an agent to run tests and propose PRs.
Codex — Cons
- Higher computational cost for agentic workflows.
- Risk of generating insecure or buggy code if unsupervised.
- Requires strong governance and sandboxing.
FAQs
A: No. InstructGPT is tuned for natural-language instruction following. Codex is optimized for code generation and engineering workflows.
A: Yes. A common pattern is: plan with InstructGPT, generate and implement with Codex, and validate in CI with tests and human review.
A: For general user-facing tasks, InstructGPT’s RLHF tuning reduces harmful outputs. For code-related user flows, Codex must be sandboxed and gated.
A: Estimate tokens per workflow (prompt + response), multiply by expected volume, and add compute for agentic runs. Run a small pilot (the six tests) to produce real numbers.
A: Redact secrets, sandbox code execution, require test gates for generated PRs, run SAST, and maintain human signoff for production merges.
Conclusion
InstructGPT and Codex are complementary tools. InstructGPT excels at natural-language tasks: summarization, specification writing, and safe public-facing assistants. Codex shines in code-first workflows: creating tests, refactoring multi-file repositories, and automating PRs inside IDEs and CI. The teams that win will combine both models: plan and define with InstructGPT, implement and test with Codex, and gate changes with automated tests, SAST, and human review.
To outrank competitors and build trust, publish reproducible benchmarks, attach a public GitHub repo with harnesses and CSVs, and refresh runs quarterly with dated changelogs. Start with the six tests in this guide, attach them to a public repo, and publish dated results — that transparency turns a good comparison into an authoritative resource.

